Back to accreditation.
FUSIC is a fusion between the two POCUS training pathways created by the Intensive Care Society – FICE (Focused Intensive Care Echo) and CUSIC (Core Ultrasound Intensive Care). Information about the FICE element to FUSIC may be found here.
The remaining elements of this pathway cover US assessment of various other systems:
- Lung ultrasound
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Vascular access ultrasound
- DVT ultrasound
The aim of merging the training pathways is to provide a modular system whereby clinicians may be accredited in the individual disciplines that are most applicable to their daily clinical practice. You may become accredited in lung ultrasound without requiring the abdominal or vascular scanning previously required for accreditation.
A link to the ICS FUSIC website it here.
The process will follow the same pathway as the FICE accreditation:
- Register with ICS using link above (involves a fee per module nowadays).
- Find a local mentor and supervisor. Lists on the website.
- Complete the ICE-BLU e-learning.
- Attend a course.
- Supervised scans.
- Unsupervised scans to complete a logbook in each module.
- Triggered assessments.
When considering which modules to complete consider which are most relevant to your daily job. Many Intensive Care doctors will never perform any abdominal ultrasound. Medical doctors may require abdominal scanning for renal scanning in AKI or for frequent abdominal paracentesis. Conversely, few people outside of Intensive Care regularly insert central lines within the UK so accruing enough scans to complete the logbook may be challenging. This new iteration of the pathways has enabled individual accreditation for areas which are most relevant to individual clinicians.
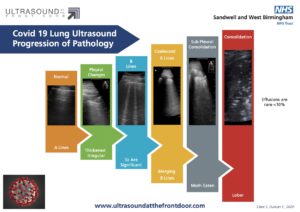
Lung ultrasound focuses on the identification of pneumothorax, pleural effusions, pneumonia and interstitial syndrome including pulmonary oedema, pneumonitis, ARDS and pulmonary fibrosis.
Abdominal ultrasound predominantly aims to identify free fluid, location for paracentesis and assess the renal tract for hydronephrosis.
Vascular ultrasound is separated into two separate modules and is targeted at safe vascular access and identification of DVTs.
Completing these modules provides credibility in the use of ultrasound in each of these disciplines and may be vital for justifying competence in performing invasive procedures. The number of mentors/supervisors is increasing and after the supervised scans most may be done remotely. Consider using a website such as sonoclipshare for remote supervision…it has worked well for me supervising trainees so far.